Tangential Induced Stress#
The induced stress is defined as the maximum tangential stress acting parallel to the exposed surface at the stope boundary.
The induced stress acting on a stope wall is best estimated by numerical modelling. When such models are not available, Mathews (1981) [1] provided two graphs which describe the stresses induced in the roof and walls of isolated openings. Potvin (1988) [2], making use of his updated database, developed his own curves for induced stress estimation. Later, Vallejos et al (2018) [3] proposed new curves based on tridimensional modelling.
Mathews Curves#
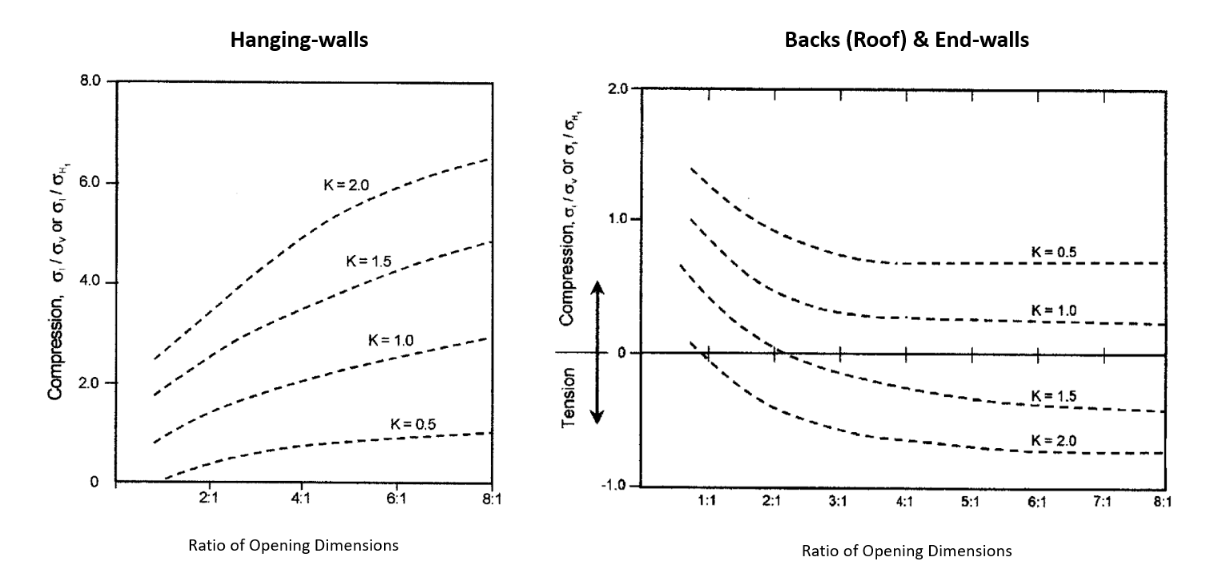
Figure 1: Stress curves proposed by Stewart and Forsyth [4], after Mathews et al [1].#
Potvin Curves#
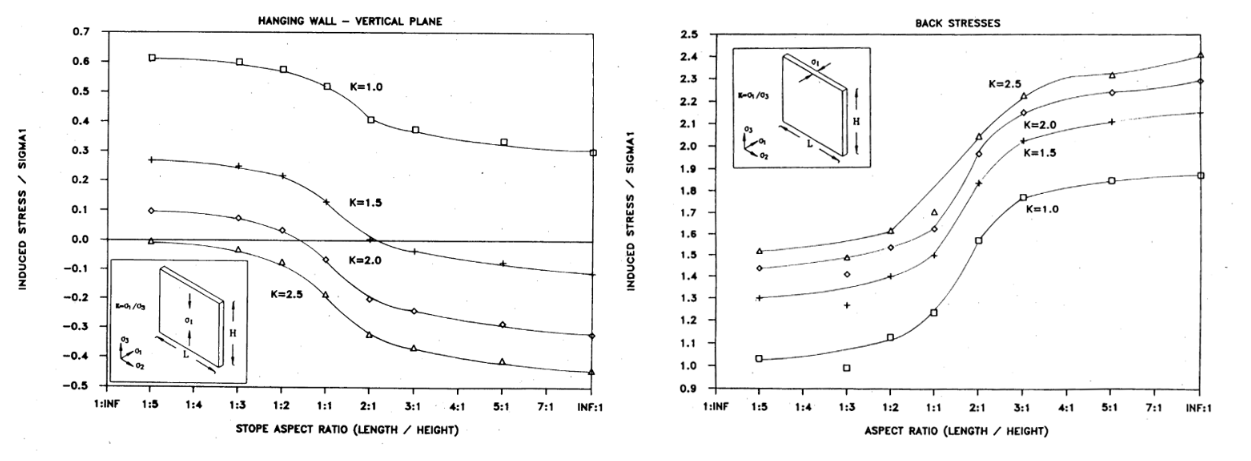
Vallejos Curves#
IMG
GeoAssistant Implementation#
Recipe#
GeoAssistant works by the word of maximum automatization, meaning that the user doesn’t have to actually call a method to calculate the induced stress of a certain stope wall. Actually, GeoAssistant detects when the necessary inputs are set and automatically calculates the induced stress.
from geoassistant import Stope
stress_tensor = Stress.createStressTensorByDepth(depth=500, density=2.7e6)
stope = Stope.createFromBlock(block=Block(corners=[[0, 0, 0], [width, length, height]]))
stope.setStressTensor(stress_tensor=stress_tensor)
roof = stope.getRoof()
induced_stress = roof.getInducedStress()